Predicting In Vitro Dissolution of Extended Release Drugs from In Vivo Profiles
Learn how Biopharmetrics successfully predicted in vitro dissolution for extended-release formulations using in vivo profiles of immediate-release drugs.
Case Study: Methodology for Predicting In Vitro Dissolution from In Vivo Profiles
Goals - Aim 1
Build a model based on literature data that:
- Describes the same literature data
- Incorporates variability in parameter values
- Can be used to simulate trials of various sizes and designs
Validate the model:
- Using literature data for comparator formulation
- Adjusting formulation parameters as necessary
- Compare simulated data to comparator formulation
Base PK Model & Noncompartmental Analysis of Predictions
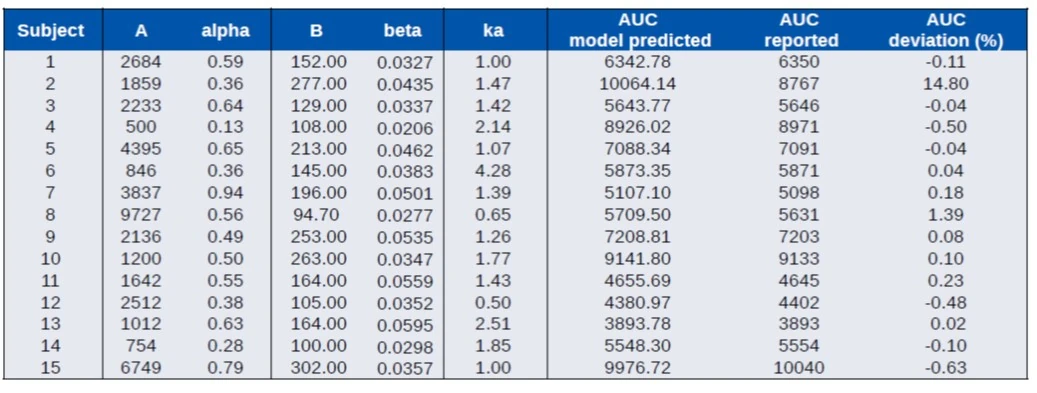
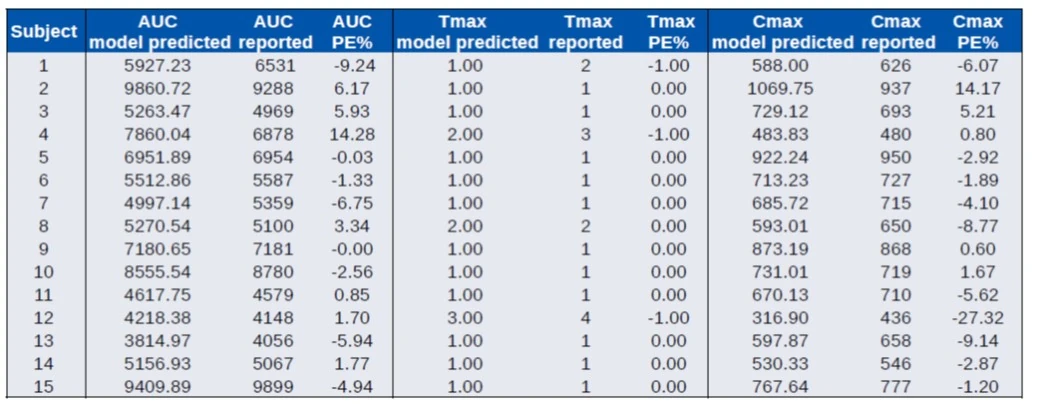
Data extracted from Colburn et al, 1983
- IR formulation (suspension) in 15 white males
- Macro constant parameters available for each subject
- Compare model predicted AUC to reported AUC (subject 2 may have a misreported parameter)
- Compare NCA of predicted profiles to reported PK parameters
- Good overall agreement
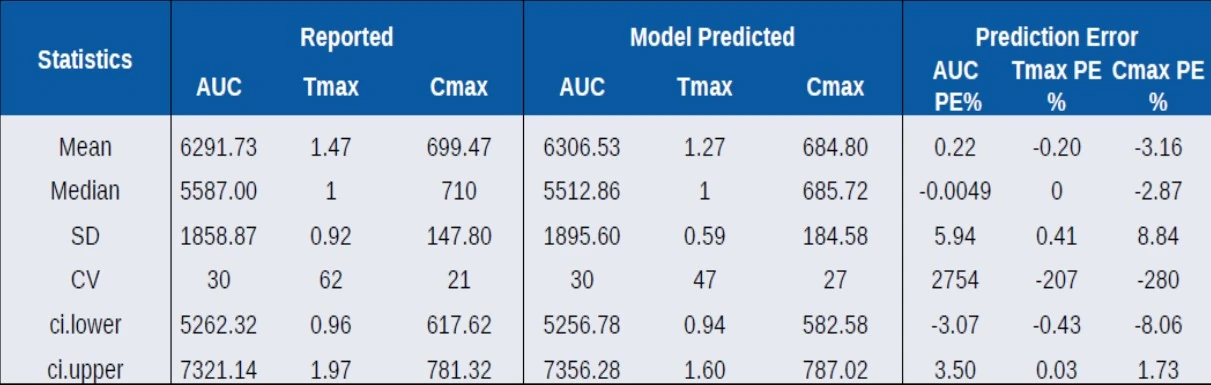
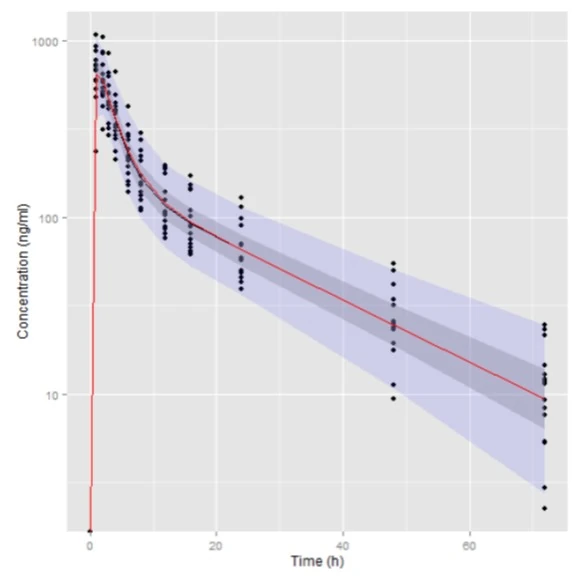
Visual Predictive Check of Base Model
Compare Distribution of NCA parameters
- PE% is small and unbiased
Goals - Aim 2
Define absorption profiles for drug QD 40 mg that are equivalent to BID 20 mg…
- On an expected value basis, so just compare medians
- For AUC and Cmin
- That have achievable manufacturing and performance
There are two types of formulations to consider:
- Slow release matrix
- Modeled with a Hill function
- Pulsatile release system (two pulses)
- Modeled with a double Weibull function
- There will NOT be an enteric coating, so dissolution will commence immediately upon administration.
- The dosage form will be ovoid with a maximum size of about 20x11 mm. A large tablet may experience prolonged and variable gastric retention time, so if dissolution is expected to differ between gastric and small intestine there could be some intersubject variability introduced
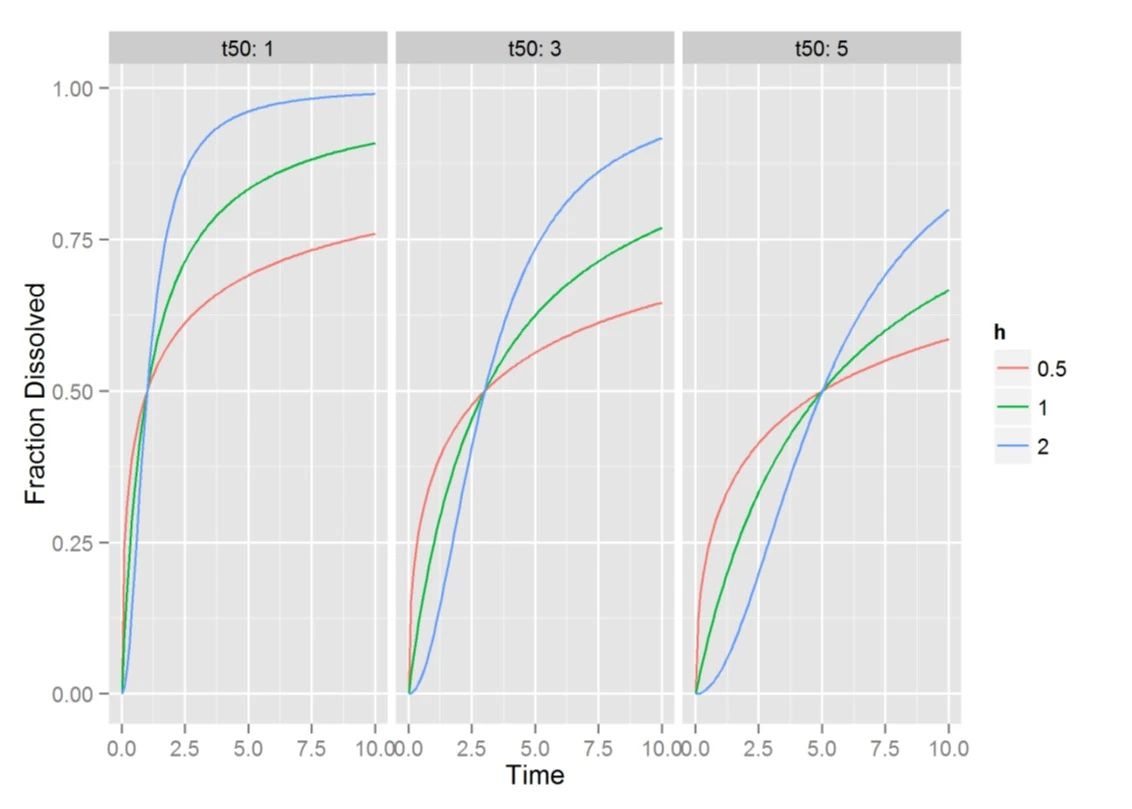
Sample Hill Function Profiles
- Cumulative dissolution function
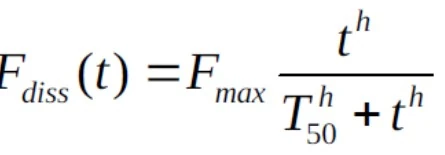
- T50 is the time to 50% absorption and h controls the amount of lag and rate of dissolution
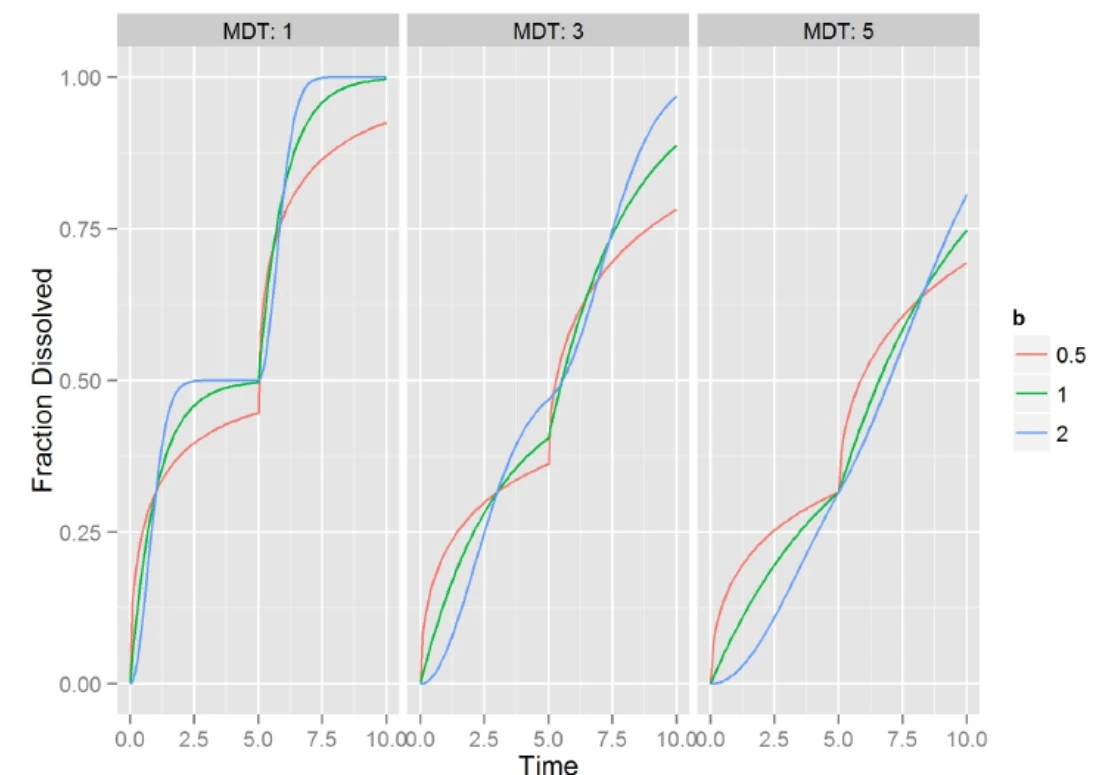
Sample Double Weibull Profile
There are two types of formulations to consider:
Note:
MDT1=MDT2=MDT
b1=b2=b
F1=0.5
Tlag2=4.5
MDT controls length of
pulse and Tlag
controls timing of
second pulse
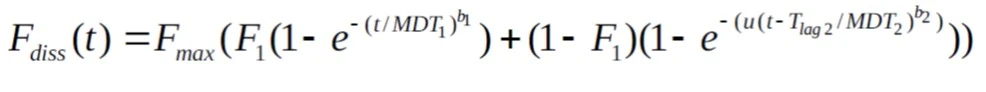
Simulation of population median response at steady state
- Compare AUC24 and Cmin between:
- Ref 20mg BID
- Target Cmin = 111.34, AUC24 = 4248.50
- Test designs
- Hill with variable T50 and b
- Hill with variable T50 and fixed b=2
- Double Weibull with variable F1,
- MDT1=MDT2=4
- Tlag=4.5 (coincides roughly with transition time to large intestine)
- b1=b2=1
- Double Weibull with variable F1, MDT2
- MDT1=2 (fast release )
- Tlag=4.5
- b1=b2=1
- Hill
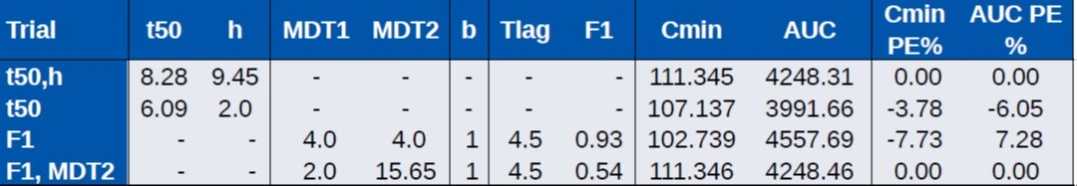
- T50,h: no prediction bias, but not a realistic formulation
- T50: realistic, but biased Cmin and AUC
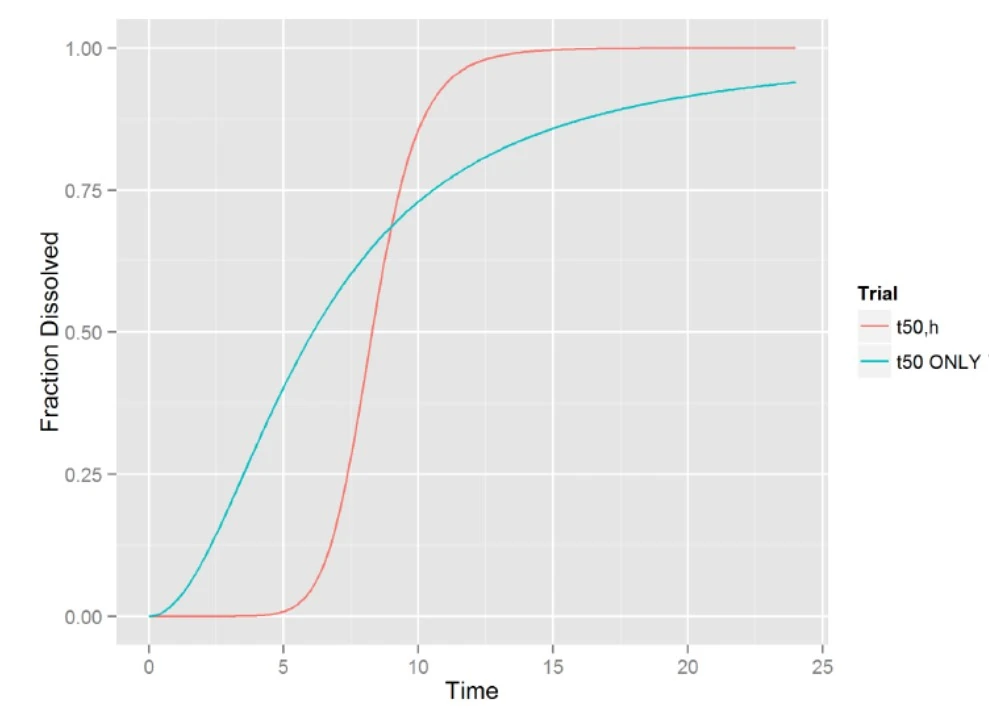
- F1: Almost all in first pulse, MDT is too fast with Tlag at 4.5
- F1, MDT2: no bias, very slow release in second pulse
- T50,h: no prediction bias, but not a realistic formulation
- T50: realistic, but biased Cmin and AUC
- How sensitive will BE be to variation in MDT2?
Optimal Hill & Double Weibull Profiles
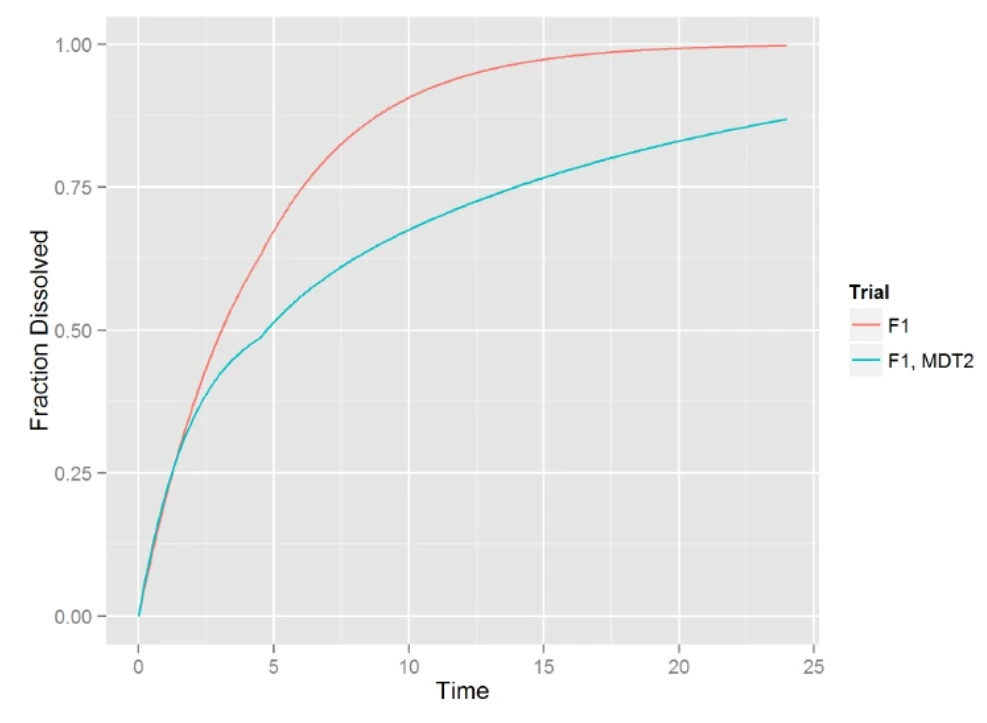
Simulated Plasma Profiles & Conclusion
A QD pulsed delivery strategy appears to achieve highest similarity to the Reference BID regimen.
- First pulse is rapid release
- Second pulse is timed to colonic delivery (Tlag~4.5 hrs) with much slower release/absorption rate (MDT~16 hrs)
- Risks
- Fraction of dose absorbed may be highly variable due to slow release required to sustain concentrations to Cmin.
- This is a problem for any of the formulations examined here. Having an initial pulse helps to ensure that at least ~50% of the dose is absorbed.
- Relative bioavailability of CR formulations may be very different than Reference
- This will have a huge impact on in vivo results
- In vitro performance may not predict in vivo performance
- It will be important to use a bio-relevant dissolution protocol when assessing formulations in vitro
Who We Are
Pioneering Drug Development: Biopharmetrics Consultancy
At Biopharmetrics, we are dedicated to empowering the pharmaceutical industry through our consultancy services. With a focus on navigating uncertainties in research and regulatory inquiries, we provide expert guidance that fosters confidence in the development of groundbreaking medicines, ultimately enhancing the lives of patients worldwide.



















Frequently Asked Question?
Understanding Our Services Through Case Studies
How does Biopharmetrics utilize in vivo profiles to predict in vitro dissolution for extended-release drugs?
At Biopharmetrics, we employ sophisticated modeling techniques that integrate in vivo data with literature insights to build predictive models. These models not only describe literature data but also incorporate variability in parameter values, allowing simulations of trials of varying sizes and designs. By validating these models against comparator formulations and adjusting formulation parameters as necessary, we ensure accurate predictions of in vitro dissolution from in vivo profiles.
What methodologies does Biopharmetrics employ in predicting absorption profiles for extended-release drug formulations?
Biopharmetrics employs a range of methodologies tailored to the specific needs of each formulation. For instance, we define absorption profiles for different formulations, such as slow-release matrices and pulsatile release systems, using techniques like Hill functions and double Weibull functions. These models account for factors like dissolution kinetics, manufacturing feasibility, and performance expectations, ensuring that the predicted profiles align with desired clinical outcomes.
How does Biopharmetrics address the challenges of variability and formulation optimization in predicting drug release kinetics?
At Biopharmetrics, we recognize the importance of addressing variability and optimizing formulations to ensure reliable predictions of drug release kinetics. Through meticulous sensitivity analysis and formulation optimization, we identify and mitigate biases in predictions while maximizing the similarity of simulated plasma profiles to reference regimens. Our approach considers factors like variation in median dissolution time (MDT), pulse timing, and release rates to develop robust formulations that meet both regulatory requirements and therapeutic objectives.
Testimonials
Discover What Our Clients Have to Say
We had an outstanding experience working with Biopharmetrics. Their deep expertise in PBPK Modelling & Simulation was evident from the start of the mAb project. The Clinical Pharmacology consultancy support in clarifying queries from the Regulatory Agency and Principal Investigator of our upcoming trial was helpful. The team’s dedication to our project, attention to detail and strict adherence to our timelines helped us achieve our goals ahead of schedule. They worked closely as part of the regular project team and took utmost care in proposing any solutions. We appreciate their commitment and highly recommend Biopharmetrics for anyone seeking PBPK Services." - Battery Bio at Vial

We engaged Biopharmetrics for IVIVC services for our products and continue to work with them, they have been very proactive in proposing solutions like optimizing the dissolution profile, selecting bio-relevant dissolution media based on pilot bio results and shortlisting the pilot batches for pivotal BE studies. Their experience in using mathematical modelling tools ie IVIVC and PBPK for predictions has helped us immensely. They have been an integral part of R&D projects, working closely with CFT’s and aligning the deliverables as per our timelines. We recommend Biopharmetrics to others who are experiencing challenges in their formulation R&D

Appcure Labs, USA& India

